Considering knee replacement surgery to relieve chronic knee pain? This post covers the essentials of knee replacement, including the procedure, recovery process, and long-term outcomes.
Key Takeaways
- Knee replacement surgery involves replacing damaged joint parts with artificial components to relieve pain and improve mobility.
- There are two main types of knee replacement: total and partial, with partial replacements allowing for quicker recovery due to less invasive procedures.
- Recovery spans about a year, with most patients resuming daily activities within six weeks, supported by physical therapy and gradual reintroduction of activities.
Understanding Knee Replacement Surgery
Knee replacement surgery, also known as knee arthroplasty, involves replacing damaged knee joint parts with artificial components made of metal and plastic. The goal is to relieve pain and improve mobility. Arthritis, especially among older individuals, is the leading cause of knee pain that necessitates knee replacement surgery.
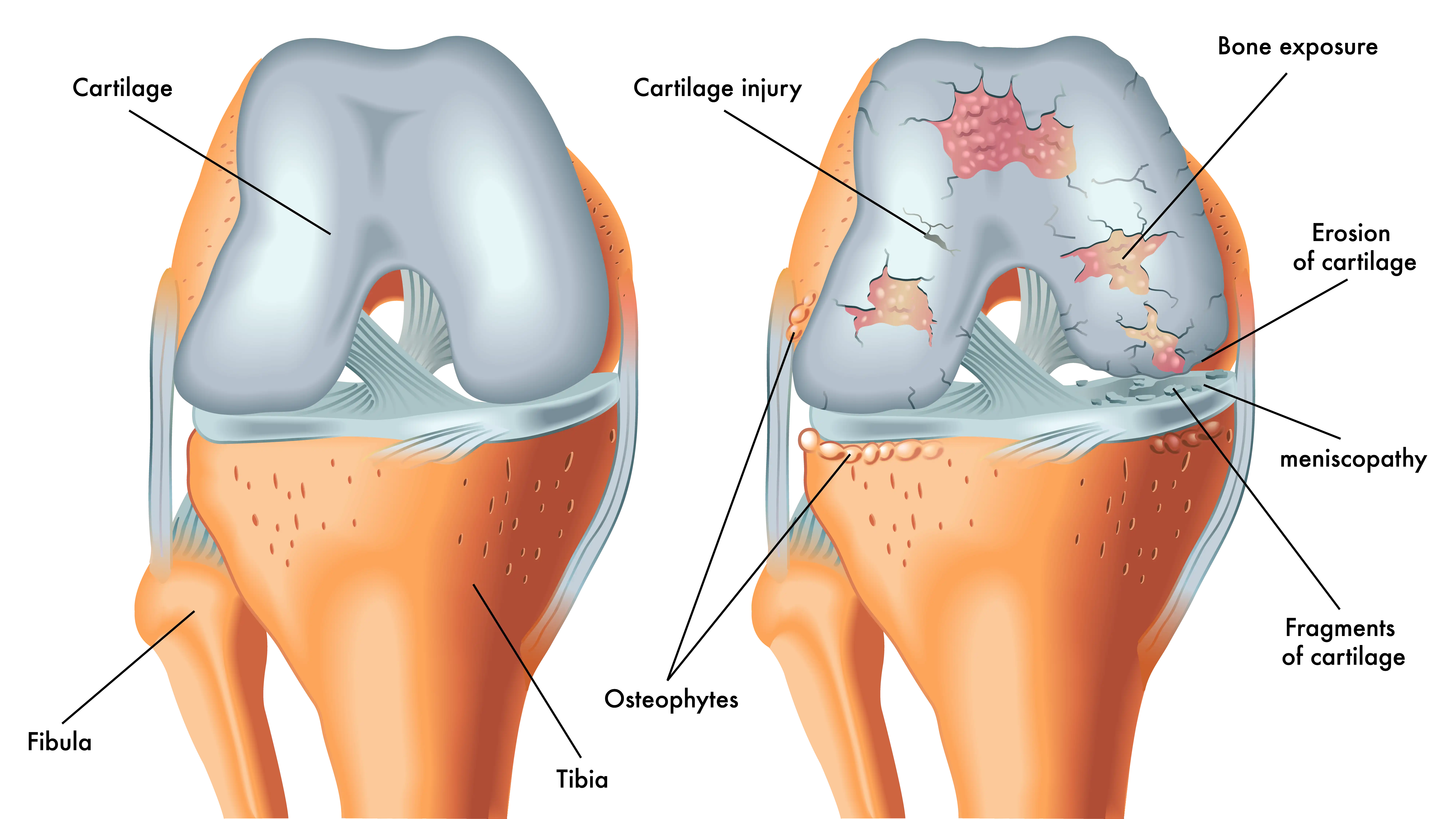
In the procedure, the orthopedic surgeon removes damaged bone and cartilage and replaces them with an artificial joint that mimics the function of a healthy knee. For many patients with chronic knee pain, the surgery has been shown to improve quality of life.
Conditions Treated by Knee Replacement Surgery
The primary condition treated by knee replacement surgery is osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease that is the leading cause of knee pain and disability. Osteoarthritis causes the cartilage in the knee joint to wear away, often leading to pain, swelling, and reduced mobility. Knee replacement surgery may become a viable option when other treatments fail to provide relief.
Aside from osteoarthritis, other conditions that may necessitate knee replacement include rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and various knee injuries. These conditions can cause significant knee damage, making daily activities difficult.
Types of Knee Replacement Surgeries
The two primary types of knee replacement surgeries are total and partial knee replacements. Total knee replacements are more common and involve replacing all damaged parts of the knee joint, whereas partial knee replacements target only the damaged area, preserving healthy cartilage and bone.
Total Knee Replacement
Total knee replacement surgery involves replacing both sides of the knee joint with metal and plastic components, effectively creating a new knee. This procedure typically takes 1 to 3 hours and can be performed by an experienced orthopedic surgeon.
This type of joint replacement is particularly effective for patients with extensive knee damage.
Partial Knee Replacement
Partial knee replacement replaces only one side of the knee joint, suitable for patients with damage limited to a specific area. About 1 in 4 people with osteoarthritis are candidates for this option.
Robotic-Assisted Knee Replacement
Robotic-assisted knee replacement is a modern surgical option that uses computer-assisted technology to help orthopedic surgeons perform knee replacement with enhanced precision. While the procedure itself is still performed by the surgeon, the robotic system provides detailed, real-time feedback and 3D imaging to help ensure accurate alignment and placement of the knee implant.
This technique may offer benefits such as:
- Improved implant positioning
- Smaller incisions and less disruption to surrounding tissue
- Potentially faster recovery times and reduced post-operative pain
Not every patient is a candidate for robotic-assisted surgery, and outcomes can vary based on individual anatomy and the extent of joint damage. Your orthopedic surgeon can help determine whether this approach is appropriate for you.
Preparing for Knee Replacement Surgery
Preparing for knee replacement surgery includes several steps to help support the best possible outcome. Specific instructions will be provided by your orthopedic surgeon, but typically, preoperative assessments along with medication and diet restrictions are involved.
Preoperative Assessments
Patients may undergo one or more preoperative assessments to ensure they are ready for surgery. Bringing a list of current medications along with medical history to the preoperative assessment is important.
Medication and Diet Restrictions
Patients will likely be instructed to discontinue certain medications and dietary supplements before knee replacement surgery to reduce complications. Many dietary supplements should be stopped seven days prior, and NSAIDs should be halted a week before surgery to reduce blood loss.
Patients are also typically advised to avoid food and drink after midnight on the day of surgery to prepare for anesthesia.
The Surgical Procedure
On the day of surgery, patients meet with the surgeon and anesthetist to discuss the procedure and anesthesia options.
During the procedure, damaged cartilage and bone may be removed, and artificial parts are attached, resurfacing the joint with metal and plastic components to create an artificial knee joint. The procedure typically takes 1 to 3 hours, depending on the complexity of the case.
The metal and plastic parts mimic the function of a healthy knee, aiming to provide long-lasting pain relief. This procedure has helped many individuals regain mobility and improve their quality of life.
Post-Surgery Recovery
Recovery after knee replacement surgery generally spans around a year, though most patients can resume daily activities within six weeks. Physical therapy plays a key role in improving function and reducing pain.
Medications, such as anti-inflammatory drugs, are often used to manage symptoms and ease pain.
Immediate Postoperative Care
Immediately after surgery, patients are taken to the recovery room where a combination of prescription pain medication, NSAIDs, and acetaminophen may be recommended for pain management. Some pain is normal, especially in the first weeks following surgery.
Physical therapy to strengthen the knee typically begins the day after surgery. Walking often begins within 12-24 hours, with many patients walking independently after about a week. A passive motion machine may be used to restore movement, decrease swelling, and improve circulation in the knee and leg.
Home Recovery Tips
To help regain mobility, aids like a cane or walker play an important role along with engaging in physiotherapy for several months with a physical therapist.
Avoiding heavy household tasks, standing for long periods, and bending down during the first 6 weeks is recommended. Having a friend or relative help with daily tasks during the first week is advisable. Light house chores can generally be resumed after 3 months.
Life After Knee Replacement
Many patients experience improvements in mobility and reduced pain following knee replacement surgery, helping them to return to normal activities.
Expected Improvements
Pain and swelling may take up to 3 months to settle, with the most intense pain occurring in the first few weeks of recovery. Improvements in mobility may be seen soon after surgery, with many patients returning to most normal daily activities within 3 to 6 weeks.
Longevity of Knee Replacements
With appropriate care, knee replacements may last 15 to 20 years, and studies suggest that around 98% of total knee replacements remain functional after a decade. Advancements in materials help to enhance the longevity of implants by reducing wear. Proper alignment during surgery can help further improve the lifespan of knee implants.
Summary
By understanding the types of knee replacement surgeries, preparation, recovery, and long-term care, patients can make informed decisions about their treatment. Advanced materials and surgical techniques continue to enhance the longevity of knee replacements, helping to provide lasting relief. For qualified patients, knee replacement surgery can help restore functionality and bring back the joy of movement.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is knee replacement surgery?
Knee replacement surgery, or knee arthroplasty, is a procedure that replaces damaged knee joint components with artificial ones to alleviate pain and enhance mobility. This surgery has been shown to improve quality of life for many patients suffering from severe and persistent knee issues.
What conditions are treated by knee replacement surgery?
Knee replacement surgery is primarily performed to treat conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and significant knee injuries that result in severe pain and joint damage.
What are the different types of knee replacement surgeries?
The main types of knee replacement surgeries are total knee replacement, which replaces the entire damaged joint, and partial knee replacement, which targets only the damaged area while preserving healthy tissue. Understanding these options can help you make an informed decision about your treatment.
What should I expect during recovery from knee replacement surgery?
You can expect recovery from knee replacement surgery to take about a year, with significant progress typically within six weeks. Engaging in physical therapy and managing pain effectively are essential for a successful recovery.
How long do knee replacements typically last?
Knee replacements typically last between 15 and 20 years, with about 98% remaining functional after the first decade. Maintaining proper care can help extend their lifespan.





