Can a torn rotator cuff heal on its own? This is the pressing question for anyone dealing with this shoulder injury. The reality hinges on multiple factors, including the nature of the tear and your health profile.
This blog post will offer insights into the healing process, explores non-surgical treatments, and advises on when to seek expert care, without promoting self-diagnosis or treatment delay.
Key Takeaways
- Rotator cuff tears, ranging from partial to complete detachment, can be caused by wear and tear, overhead activities, heavy lifting, or acute incidents, with the supraspinatus tendon being most vulnerable.
- Non-surgical treatments like rest, ice, physical therapy, steroid injections, and anti-inflammatory medications are often effective for rotator cuff recovery, but surgical intervention is necessary for more severe or complicated injuries.
- Lifestyle modifications, including dietary adjustments to promote collagen synthesis and adapting activities to minimize stress on the shoulder, can support the healing of a torn rotator cuff, complementing medical treatments.
Exploring the Rotator Cuff: A Primer
The rotator cuff, a group of four rotator cuff muscles nestled in our shoulder joint, plays a vital role in our daily activities. These muscles include:
- Subscapularis
- Supraspinatus
- Infraspinatus
- Teres minor
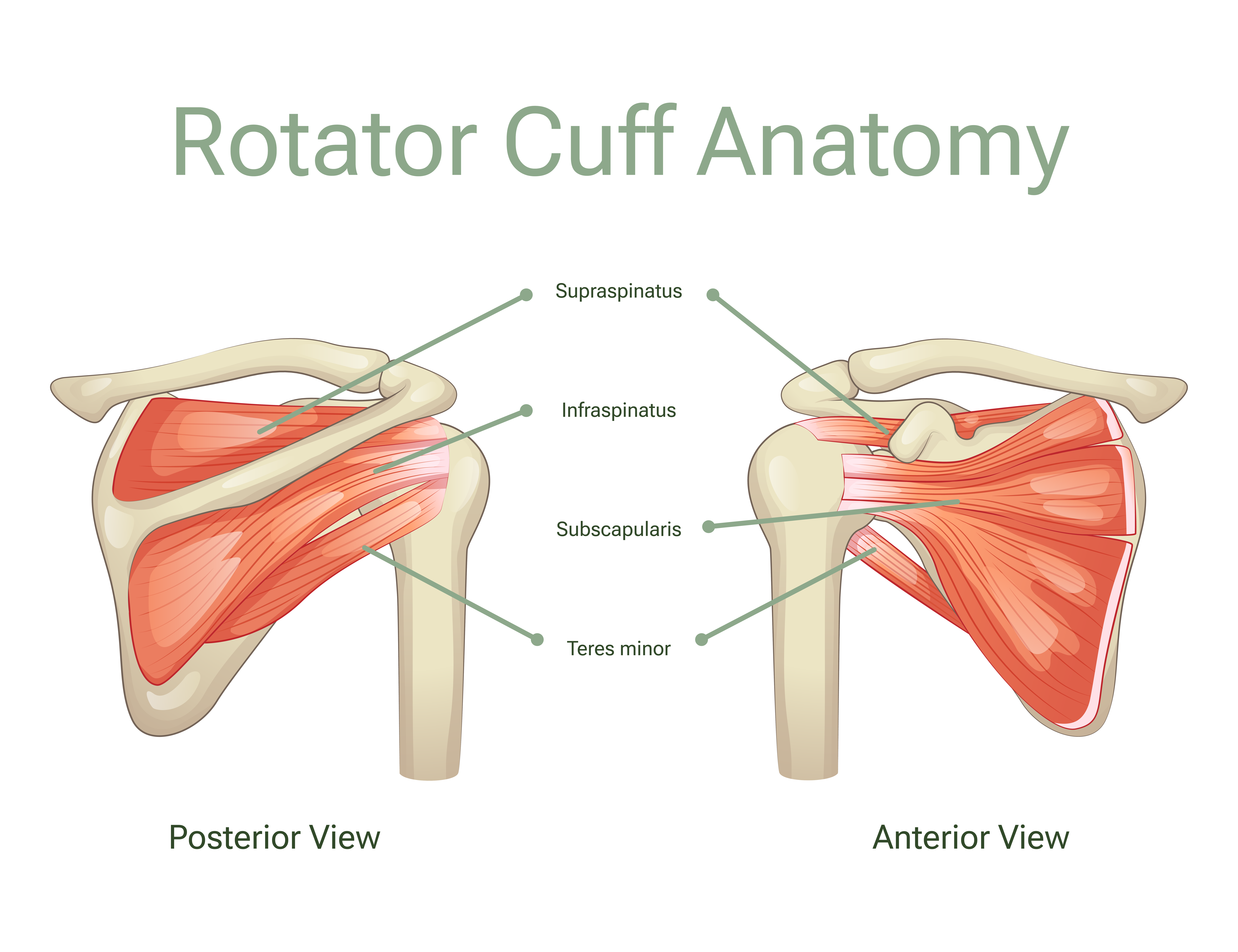
Each muscle has a unique role, contributing to the overall functionality of the shoulder. To prevent rotator cuff injuries that lead to shoulder pain and restricted arm mobility, one must grasp the intricacies of this structure.
The Reality of Rotator Cuff Tears
Rotator cuff tears, a common type of rotator cuff injuries, can be a real pain in the shoulder. These can range from strain and partial tears, where the tendon is not completely severed, to full-thickness tears where the tendon detaches from the bone completely. Experiencing rotator cuff tear symptoms like shoulder pain and arm pain could indicate a potential rotator cuff injury.
The causes of these tears can be diverse, including:
- wear and tear
- overhead activity
- heavy lifting
- acute incidents like falls or accidents
The supraspinatus tendon is the most susceptible to tears, making it a prime focus in rotator cuff repair.
Healing Potential of Rotator Cuff Injuries
Various factors that determine the healing potential of a torn rotator cuff include:
- The size of the tear
- The shoulder’s functional ability
- The individual’s overall health
- Age (older individuals typically have less capacity for natural repair)
Larger tears also present a challenge in healing, often necessitating surgical intervention.
Conservative Measures for Rotator Cuff Recovery
Although some cases necessitate surgical intervention, in many instances, conservative or non-surgical treatments prove effective. These measures aim to reduce pain and restore functionality to the shoulder by relying on:
- Rest
- Ice
- Physical therapy
- Steroid injections
- Anti-inflammatory medications
Rest and Pain Management
The initial phase of conservative treatment involves rest, which is vital to reduce inflammation and promote healing. Avoiding activities that exacerbate the injury and taking breaks can significantly contribute to the healing process.
To manage pain and inflammation, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can be beneficial. Over-the-counter medications such as acetaminophen and ibuprofen can be used to alleviate shoulder pain related to rotator cuff injuries.
Physical Therapy’s Role
Physical therapy is integral to rotator cuff recovery as it seeks to rectify physical impairments causing pain and dysfunction while enhancing shoulder movement, flexibility, muscle balance, and stability. A comprehensive physical therapy regimen includes different phases of exercises, starting from immobilization to strengthening exercises with added resistance.
Specific exercises and stretches, like pendulum exercises, active-assisted exercises, and stretches for the posterior capsule and pectoralis minor, are recommended. These exercises facilitate optimal motor patterning and encourage the release of endorphins to reduce muscle tension. Hands-on manual therapy and massage therapy may also be included in physical therapy sessions to loosen tight muscles, increase flexibility, and enhance overall shoulder recovery.
When Surgery Becomes an Option
For more severe or complicated injuries, surgery may come into play if nonoperative treatments do not yield improvement. Active patients with a complete tear of the tendon often consider rotator cuff surgery as it offers the most predictable way to help a rotator cuff tear heal and restore function.
Arthroscopic surgery is a minimally invasive approach to rotator cuff repair that typically results in decreased pain and quicker recovery compared to traditional open surgery methods.
Recovery Process Post-Surgery
During the initial recovery phase post-surgery, patients typically adorn a sling or splint and participate in passive motion exercises. Recovery time can vary significantly, with most individuals regaining full range of motion and strength within 4 to 6 months. However, factors such as larger tears, lower quality tendon tissue, unhealthy lifestyle choices, age, and noncompliance with rehabilitation protocols can extend recovery durations.
Despite the challenges, rotator cuff surgeries have a high success rate, with most patients returning to their usual activities following adequate recovery and rehabilitation.
Lifestyle Adjustments to Support Healing
Apart from medical treatments, specific lifestyle modifications can aid in the healing of a torn rotator cuff. Here are some recommendations:
- Increase the intake of vitamin C, protein, glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate, and certain minerals to promote collagen synthesis and aid in the healing process.
- Consider taking anti-inflammatory supplements such as turmeric, ginger, and omega-3 fatty acids, but make sure to consult a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements.
- Ensure you are getting enough amino acids from food and supplements, as they are vital for collagen formation crucial for tendon repair.
Minimizing stress on the injured rotator cuff tendon is also critical. This involves avoiding lifting weights overhead, taking breaks during repetitive shoulder movements, and utilizing adaptive tools where necessary. The application of heat therapy can relieve pain and improve blood circulation to the rotator cuff, enhancing healing.
Moreover, aromatherapy using essential oils such as lavender, peppermint, ginger, and rosemary can potentially reduce inflammation and muscle tension, aiding in the alleviation of rotator cuff pain. Adopting sleep positions that alleviate pressure on the injured rotator cuff can also contribute to the healing process.
Recognizing When to Seek Professional Help
A persistent, dull ache in the shoulder that worsens at night or disrupts sleep might signal a severe rotator cuff issue demanding professional attention. Difficulties with daily activities, such as combing hair or reaching behind the back, along with arm weakness, should also trigger a visit to a healthcare professional, even in the absence of pain. Ignoring treatment for a rotator cuff injury can lead to permanent loss of motion or consistent weakness, and a torn tendon may retract, complicating future treatment and reducing the chance of a successful outcome.
Persistent post-surgery pain should also not be overlooked as it may indicate serious complications requiring immediate medical attention. In severe cases, patients experiencing severe pain are often referred to an orthopedic surgeon, who might recommend surgery based on the specific condition and symptoms.
Summary
In conclusion, understanding the anatomy and functioning of the rotator cuff, the reality of rotator cuff tears, and the healing potential of these injuries can significantly contribute to effective treatment and recovery. While conservative measures like rest, pain management, and physical therapy play a crucial role in recovery, severe or complicated injuries may require surgical intervention. Supporting healing through lifestyle adjustments and recognizing when to seek professional help are equally important.
The journey to recovery may be challenging, but with the right knowledge, treatment, and care, you can regain the full function and strength of your shoulder.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens if a torn rotator cuff goes untreated?
Untreated torn rotator cuff can lead to restricted function, limited range of motion, and potential progression to total tears, which may result in arthritis. It is important to seek treatment to avoid these complications.
What happens if you don’t fix a torn rotator?
If left untreated, a torn rotator cuff can lead to increased pain, reduced range of motion, and diminished shoulder strength, impacting daily activities. It’s crucial to seek medical advice to prevent these complications.
What are 2 warning signs of a rotator cuff tear?
The two warning signs of a rotator cuff tear are shoulder pain and weakness. It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience these symptoms.
What causes a rotator cuff tear?
Rotator cuff tears can occur due to repetitive wear and tear, overhead activity, heavy lifting, and acute incidents such as falls or accidents. These factors can lead to the tear in the rotator cuff.





