Pain behind the knee can range from a minor inconvenience to a serious issue. Understanding its causes and treatment options is important for relief. This post explores why you might have pain behind the knee and what you can do about it.
Key Takeaways
- Pain behind the knee can result from injuries, arthritis, or conditions like Baker’s cysts, with symptoms ranging from sharp pain to swelling.
- Accurate diagnosis through physical examination and imaging tests is essential for effective treatment of knee pain.
- Home management strategies, along with prevention techniques such as maintaining a healthy weight and performing knee exercises, are key to managing and reducing knee pain.
Understanding Pain Behind the Knee
Pain behind the knee, often referred to as posterior knee pain, can be a debilitating experience that affects your daily activities and overall quality of life. Chronic knee pain, defined as pain lasting three months or more, can gradually worsen and significantly impact activities you enjoy. Conversely, acute knee pain is characterized by sudden, sharp pain following an injury or trauma. Approximately 46.2% of people experience knee pain at some point in their lives, highlighting the widespread nature of this issue.
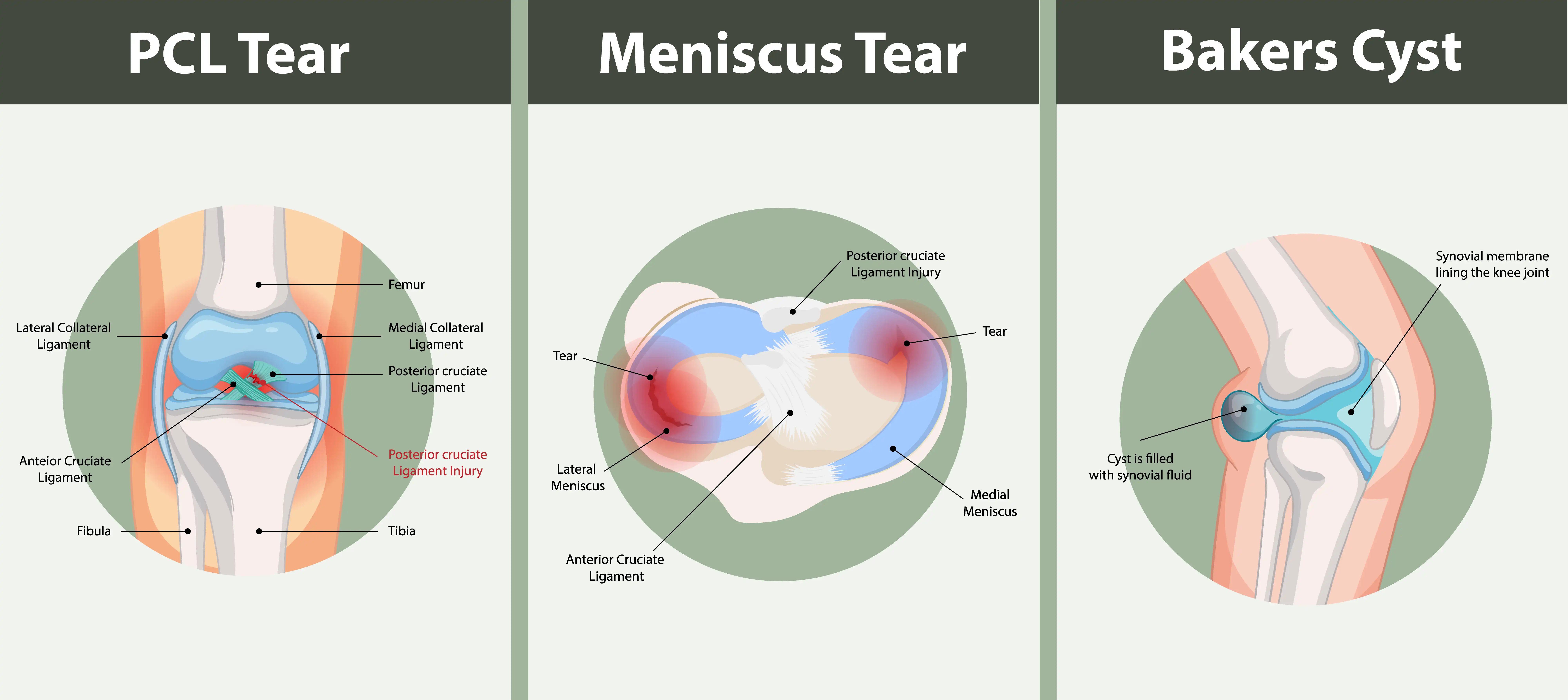
Recognizing the nature of your knee pain is pivotal for effective treatment and management. Causes of posterior knee pain range from injuries and arthritis to rare conditions like cancer. Symptoms can vary significantly, from sharp, intense pain to a persistent, dull ache.
We will now explore the specific causes and symptoms of pain behind the knee, providing insights to help you identify and address this common yet complex issue.
Posterior Knee Pain Causes
Pain behind the knee can stem from various conditions, including common knee injuries such as PCL injuries and meniscus tears. These injuries can occur during activities that involve twisting or squatting, causing significant discomfort and hindering movement. Another common cause of posterior knee pain is arthritis, a degenerative disease that leads to discomfort and stiffness in the knee joints.
In addition to injuries and arthritis, conditions like Baker’s cysts can also lead to pain behind the knee. A Baker’s cyst, often associated with other knee problems, involves fluid accumulation in the joint, causing a noticeable bulge and discomfort in the back of the knee.
Anatomical issues, such as abnormal tracking of the kneecap, can further contribute to knee pain by affecting the natural movement and alignment of the knee joint. Recognizing these causes aids in effective treatment and prevention. Identifying your pain triggers can help you take proactive steps to manage and prevent knee pain.
Common Symptoms
Common symptoms of acute knee pain include:
- Sharp, intense, localized pain, which may sometimes have a burning sensation
- Swelling from an acute injury, which could indicate a ligament injury or fracture
- Restricted movement of the leg, making it difficult to bend properly
- Swelling behind the knee, which may be localized to the back of the knee or extend into the calf, further complicating movement and daily activities.
Chronic knee pain, on the other hand, is often described as a dull ache that can become sharp during worsened conditions. This type of pain is usually accompanied by persistent weakness in the knee joint and may lead to joint mobility being significantly limited due to knee hurt and swelling.
Common causes of chronic knee pain include:
- Osteoarthritis, which can cause pain and stiffness due to cartilage breakdown
- Tendinitis, which is inflammation of the tendons around the knee
- Bursitis, which is inflammation of the small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the knee joint
- Meniscus tears, which can occur from injury or degeneration over time
These conditions can ultimately lead to swelling and restricted movement.
Early recognition of these symptoms can prompt timely medical attention, preventing further damage. Whether it’s swelling, sharp pain, or a dull ache, understanding these signs can guide you in managing and alleviating pain.
Key Conditions Leading to Pain Behind the Knee
Acute injuries and chronic knee issues often lead to swelling and pain in the knee area, significantly impacting one’s mobility and quality of life. Conditions such as osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are major contributors to knee swelling and discomfort, exacerbated by factors like weather changes that affect fluid levels in the knee. Pain behind the knee can arise from various health conditions, signaling underlying issues that require attention.
Identifying the underlying cause of your knee pain is essential for effective treatment. Here, we’ll explore three key conditions that commonly cause pain behind the knee: Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) injuries, Baker’s cysts, and osteoarthritis.
Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Injuries
Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) injuries can occur from overstretching or tearing due to impactful force on a bent knee. Common situations that lead to PCL injuries include hitting the knee on a dashboard during a car accident or hyperextending the knee during sports activities. These injuries often result in significant knee pain and instability, which can complicate your ability to perform daily tasks or participate in physical activities.
Ignoring a PCL injury can result in later complications, affecting knee stability and function. Addressing these injuries promptly helps prevent long-term issues and ensures proper healing.
Baker’s Cyst
A Baker’s cyst, also known as a popliteal cyst, is a fluid-filled sac that forms in the back of the knee. This cyst often develops from knee injuries, leading to swelling and discomfort in the posterior region. When the knee is injured, fluid accumulates in the joint, exacerbating the condition and causing a noticeable bulge at the back of the knee.
Sensations of a Baker’s cyst can be felt in the depression at the back of the knee, making it uncomfortable to bend or straighten the leg. Accurate diagnosis and treatment are essential for managing this condition and preventing further complications.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a condition that commonly leads to pain behind the knee due to cartilage deterioration. This condition can contribute to patellofemoral pain syndrome, although this syndrome can also occur independently. While osteoarthritis often affects the medial compartment of the knee, causing significant discomfort and mobility issues, not all areas of the knee are necessarily impacted.
The likelihood of developing osteoarthritis increases for individuals over the age of 50, making it a prevalent concern for older adults. Both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis can affect the back of the knee, causing pain and swelling that limit joint mobility.
Understanding and managing these conditions is key to maintaining knee health and preventing further deterioration.
Diagnosing Pain Behind the Knee
Accurate diagnosis is key for effective knee pain treatment. A thorough examination includes discussing your medical history and symptoms to pinpoint the cause. Diagnostic tests determine underlying issues and help develop an effective treatment plan. Clinical evaluations are vital for accurate diagnosis and guiding treatment options.
In the following subsections, we will explore the physical examination and imaging tests that are commonly used to diagnose knee conditions.
Physical Examination
A physical examination helps diagnose knee pain by identifying underlying causes and assessing functionality. This comprehensive evaluation includes inspecting the knee for swelling and tenderness, and assessing range of motion.
Diagnostic procedures often include analyzing the patient’s physical condition and medical history. Overall, the knee examination plays a significant role in identifying potential causes of pain and guiding subsequent treatment options.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests are crucial for accurately diagnosing knee injuries and conditions. Common tests include X-rays and MRIs, while an ultrasound may be suggested for suspected popliteal cysts. For PCL injuries, X-rays or MRI scans might be recommended.
These imaging methods provide detailed views of the knee joint, allowing healthcare providers to identify the specific cause of pain and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Home Management Strategies for Pain Behind the Knee
Managing knee pain at home involves a comprehensive approach, including physical therapy, surgical interventions, and various alternative therapies. Treatment options range from medication and physical therapy to surgical procedures, depending on the cause and severity.
Effective home management strategies can significantly alleviate pain and enhance recovery. We will discuss specific methods like the POLICE method and the HARM protocol for managing pain behind the knee.
POLICE Method
The POLICE method stands for:
- Protect
- Optimal Loading
- Ice
- Compression
- Elevation
This method focuses on protecting the injured area while allowing for optimal loading to promote recovery. The ‘Optimal Loading’ aspect encourages gentle movement that avoids aggravating pain, helping to stimulate healing by applying appropriate mechanical stress to the injured area.
Ice helps decrease inflammation and assists in removing waste products from the injured area, while compression minimizes swelling and promotes circulation.
Employing the POLICE method can significantly aid in managing acute knee injuries and reducing pain.
HARM Protocol
Avoiding certain activities is important during early knee injury recovery. The HARM protocol advises against Heat, Alcohol, Running, and Massage during the initial recovery period.
Applying heat can increase blood flow, which can worsen swelling and inflammation. Alcohol can interfere with the body’s healing processes and may increase inflammation, making it a substance to avoid during recovery. Running can stress the injured knee joint, hindering healing. Massaging near an injured area can aggravate inflammation and may complicate the healing of the knee.
Following these recommendations can lead to a more effective recovery from knee injuries.
When to Seek Professional Help
Recognizing when knee pain requires professional evaluation helps prevent further injury. If knee pain worsens or home remedies are ineffective, seek medical attention. Persistent pain and difficulty bearing weight indicate the need for medical consultation.
In the following subsections, we will discuss specific signs of serious injury that warrant professional help and how to choose the right specialist for knee pain.
Signs of Serious Injury
Swelling, buckling, and an inability to bear weight prompt a doctor’s consultation for knee pain. These symptoms may indicate severe conditions like a blood clot, requiring immediate medical attention. Sharp or severe pain and swelling after an injury should also be taken seriously.
Ignoring these signs can lead to further damage and complications. Seek medical advice if you experience any of these symptoms to prevent worsening and ensure proper treatment.
Choosing the Right Specialist
An orthopedic surgeon with sports medicine experience is best for treating knee pain. These specialists diagnose and treat musculoskeletal issues, including knee injuries.
When choosing a doctor for knee pain, consider your symptoms’ severity and the type of care needed.
Treatment Options for Pain Behind the Knee
Various treatment options manage pain behind the knee, from conservative measures to invasive procedures. NSAIDs can reduce pain and inflammation at home, while gentle activities facilitate recovery and prevent stiffness. Consulting a physical therapist can aid in rehabilitation.
In the following subsections, we will explore physical therapy, surgical treatments, and other treatments that can help relieve knee pain and improve function.
Physical Therapy
Rehabilitation often involves physical therapy focusing on strength and stability for PCL injuries. It aims to reinforce the muscles surrounding the knee to enhance stability and alleviate pain through tailored exercises like quad sets, straight leg raises, and hip-strengthening activities.
Physical therapy for knee pain typically involves two to three sessions per week over several weeks, focusing on customized treatment plans. This approach helps relieve pain, improve mobility, and prevent future injuries.
Surgical Treatments
In severe knee pain cases, surgical treatments may be necessary to repair damage or realign the joint. Common procedures include:
- Arthroscopy, which uses minimally invasive techniques to repair tissue damage
- Partial knee replacements
- Total knee replacements
- Ligament reconstruction, which addresses severe degenerative changes
These surgeries aim to alleviate pain and restore knee joint function, allowing individuals to return to daily activities with reduced discomfort. Consulting an orthopedic surgeon helps determine the most appropriate surgical option based on severity and underlying cause.
Other Treatments
Additional treatments for knee pain include medications and injections, such as corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid, which provide temporary relief. Corticosteroid injections reduce inflammation and pain, while hyaluronic acid injections improve joint lubrication and mobility.
Alternative therapies like the use of heat or ice can also help manage pain behind the knee. These treatments can be integrated into a comprehensive plan to alleviate pain and enhance recovery.
Preventing Pain Behind the Knee
Preventing pain behind the knee involves proactive measures to maintain knee health and reduce injury risk. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Maintain a healthy body weight.
- Incorporate knee exercises.
- Wear proper footwear.
- Follow a balanced diet.
- Engage in regular physical activity to keep weight in check and alleviate knee stress.
In the following sections, we’ll take a closer look at some of these preventive strategies.
Maintaining Healthy Body Weight
Excess body weight increases stress on knee joints, heightening the risk of pain and injury. Even being slightly overweight can strain the knees, escalating the risk of joint issues. Maintaining a healthy weight minimizes stress on knee joints, preserving their longevity and function.
A balanced diet and regular physical activity are essential for maintaining a healthy weight and preventing knee pain. Combining lifestyle changes with regular exercise forms a comprehensive approach to knee pain prevention.
Knee Exercises
Targeted strengthening exercises enhance the muscles around the knee, providing better support and stability. Exercises like squats and lunges are essential for improving joint stability.
Incorporating exercises that target both the knee and surrounding muscles, like hip abductor strengthening, helps alleviate knee pain and reduce injury risk. Overall, strengthening exercises improve knee function and reduce pain.
Proper Footwear
Proper arch support and cushioning in shoes significantly reduce the risk of knee injuries during physical activities. Suitable shoes help distribute weight evenly and reduce stress on knee joints.
Supportive, well-cushioned shoes maintain proper alignment and protect knees during physical activities. Proper footwear is helpful for knee health, providing necessary support to prevent injuries.
Summary
Understanding and managing pain behind the knee involves recognizing the causes, identifying symptoms, and implementing effective treatment strategies. Proper diagnosis through physical examinations and imaging tests is important for developing an appropriate treatment plan. Home management strategies like the POLICE method and avoiding HARM activities can significantly alleviate pain and promote recovery.
Preventive measures such as maintaining a healthy body weight, performing knee exercises, and wearing proper footwear are essential for preventing knee pain and ensuring long-term knee health. By taking proactive steps and seeking professional help when necessary, you can manage and prevent pain behind the knee, leading to a more active and pain-free life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common causes of pain behind the knee?
Pain behind the knee is often caused by injuries such as PCL tears, arthritis, or the presence of a Baker’s cyst. Identifying the specific cause is crucial for effective treatment.
What symptoms should prompt a visit to the doctor for knee pain?
If you experience swelling, inability to bear weight, or persistent sharp pain in your knee, it’s important to visit a doctor for evaluation. Prompt attention can help address any underlying issues effectively.
How can physical therapy help with knee pain?
Physical therapy effectively alleviates knee pain by strengthening the surrounding muscles for improved stability and function. This targeted approach not only reduces discomfort but also enhances overall mobility.
What is the POLICE method for managing knee pain?
The POLICE method for managing knee pain consists of Protecting the injury, Optimal Loading, applying Ice, Compression, and Elevation. By following these steps, you can effectively manage acute knee injuries and promote healing.
How does maintaining a healthy body weight prevent knee pain?
Maintaining a healthy body weight significantly reduces stress on the knee joints, helping to lower the risk of pain and injury. This proactive approach can lead to improved joint health and overall well-being.





