Shoulder bursitis is the inflammation of the bursa, a fluid-filled sac that cushions your shoulder joint. This condition causes pain and restricted movement. In this post, we’ll discuss the symptoms, causes, and treatments to effectively manage shoulder bursitis.
Key Takeaways
- Shoulder bursitis is characterized by inflammation of the bursa, leading to pain and restricted movement, often caused by repetitive overhead activities.
- Symptoms include localized shoulder pain, especially at night, swelling, and limited range of motion; early recognition is crucial for effective treatment.
- Treatment options range from at-home care, like rest and ice, to professional interventions such as physical therapy and, in severe cases, surgery.
Understanding Shoulder Bursitis
Shoulder bursitis occurs when the bursa, a small fluid-filled sac that cushions the shoulder joint, becomes inflamed. Normally, the bursa helps reduce friction between tissues, but when it’s inflamed, it can cause significant pain and discomfort. In this condition, while the bursa is inflamed, it doesn’t necessarily swell up visibly.
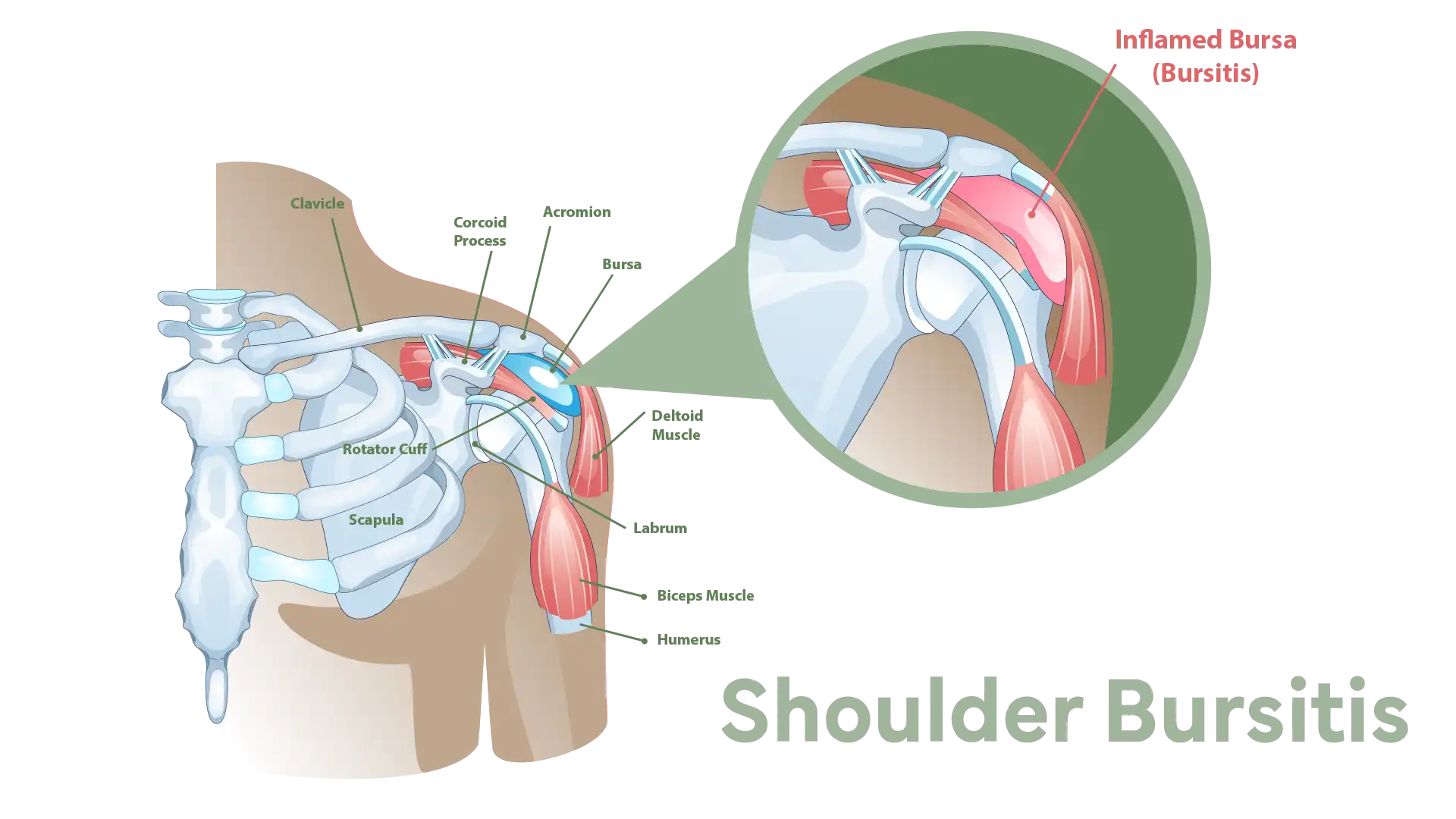
The bursa acts like a lubricant in the shoulder joint, allowing for smooth movement. However, excessive friction can cause it to thicken and produce more fluid, leading to pain and restricted movement. Grasping this process helps in understanding how this condition develops and impacts daily activities.
Appreciating the role of the bursa in shoulder mechanics clarifies why inflammation can be so debilitating. The shoulder joint is a complex structure involving the rotator cuff and shoulder blades, and any disruption due to an inflamed bursa can lead to significant discomfort and movement limitations.
Common Causes of Shoulder Bursitis
The causes of shoulder bursitis are often linked to repetitive irritation and overuse of the shoulder joint. Activities that involve repetitive overhead movements, such as painting or playing tennis, are major culprits. This constant motion increases friction in the shoulder, leading to inflammation.
Chronic bursitis typically arises from prolonged friction and can be exacerbated by underlying health conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. Over time, repetitive movements can wear down the bursa, causing long-term inflammation and pain. Professionals and athletes who frequently use their shoulders, such as carpenters and football players, are at a higher risk of developing shoulder bursitis.
Common underlying medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, can also increase the likelihood of developing shoulder bursitis. Knowing these risk factors aids both prevention and early intervention.
Recognizing Symptoms of Shoulder Bursitis
The symptoms of shoulder bursitis can range from mild to severe, but they often include localized shoulder pain that can feel like a dull ache or sharp pain. Many patients report increased pain at night, particularly when lying on the affected side. This nocturnal pain can significantly disrupt sleep and overall well-being.
Other common symptoms include swelling and tenderness around the shoulder joint, which may be accompanied by warmth. In acute traumatic bursitis, bruising might also be visible, leading to increased pain with movement. These symptoms can limit the range of motion, making activities like lifting the arm or reaching overhead particularly challenging.
Early recognition of these symptoms is key to effective treatment and management. Noticing any of these signs should prompt a medical evaluation to prevent the condition from worsening.
Types of Shoulder Bursitis
Shoulder bursitis can manifest in several forms, each with unique characteristics and causes. These include acute traumatic bursitis, chronic bursitis, and infected bursitis. Differentiating between these types is key for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Acute Traumatic Bursitis
Acute traumatic bursitis is characterized by a rapid onset of symptoms following a specific injury or trauma to the shoulder. This type of bursitis, including acute bursitis, is common in sports-related injuries where there is a direct blow or excessive joint bending, such as falling on an outstretched arm. The immediate symptoms often include swelling, tenderness, and warmth around the affected area.
Prompt attention is needed for this type of bursitis to prevent further damage and alleviate pain. Athletes and active individuals should be cautious, as acute traumatic bursitis can escalate rapidly without proper care.
Chronic Bursitis
Chronic bursitis develops over time, often due to repetitive irritation and overuse of the shoulder. This type of bursitis can be linked to underlying conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, which causes long-term inflammation in the shoulder. Older adults are more susceptible due to the cumulative effects of wear and tear over the years.
Management of chronic bursitis typically involves reducing activities that cause swelling, using anti-inflammatory medications, and applying ice to reduce inflammation. In some cases, physical therapy may be necessary to strengthen the shoulder and prevent further irritation.
Infected Bursitis
Infected bursitis is a more serious form, caused by bacterial infection within the bursa. Symptoms include:
- excessive warmth
- redness
- fever
- severe pain
If a fever accompanies bursitis symptoms, it indicates a need for immediate medical attention.
Prompt treatment is really important here to prevent the infection from spreading and causing more severe health issues. Infected bursitis often requires antibiotics and may involve draining the bursa to remove infected fluid.
Diagnosing Shoulder Bursitis
Diagnosing shoulder bursitis involves a combination of physical examination and imaging tests. During a physical exam, an orthopedic shoulder surgeon will look for signs of redness, warmth, tenderness, and swelling around the shoulder joint. They may also assess the range of motion, particularly if pain increases during elevation and rotation, which is common in subacromial bursitis.
X-rays can help identify any calcifications in the bursa that may indicate chronic bursitis. An MRI scan is particularly valuable for visualizing the bursa and confirming the diagnosis, especially in complex cases where other shoulder pathologies are suspected.
A precise diagnosis is important for creating an effective treatment plan. This is one reason I recommend seeing an orthopedic surgeon who is fellowship trained in shoulders as they have advanced training in this area that can be beneficial to patients. Knowing the specific type and severity of bursitis allows the orthopedic surgeon to recommend effective interventions to alleviate pain and restore function.
Effective Treatments for Shoulder Bursitis
Treating shoulder bursitis effectively involves a combination of at-home care and medical interventions. The goal is to reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, and restore mobility. Treatments vary based on the severity and type of bursitis, ranging from rest and ice applications to advanced medical procedures to treat bursitis.
At-Home Treatments
At-home treatments for shoulder bursitis are often the first line of defense. Here are some effective strategies:
- Resting the shoulder and avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms is crucial.
- Applying ice to the affected area for 10 to 15 minutes can help reduce inflammation and pain.
- Gentle stretching exercises are also beneficial in maintaining shoulder mobility and reducing muscle tension.
By following these steps, you can manage your shoulder bursitis effectively.
A strategy that combines rest, ice application, and stretching exercises can significantly alleviate symptoms and prevent worsening.
Medical Interventions
For more severe cases of shoulder bursitis, medical interventions may be necessary. Corticosteroid injections can quickly reduce inflammation and pain but come with risks such as a higher likelihood of tendon rupture. Physical therapy often aids recovery and restores shoulder function following initial treatment.
Surgical options may be considered if conservative treatments fail. A shoulder surgeon might remove damaged tissue or the bursa itself using arthroscopic techniques. Excision of the bursa is typically reserved for persistent cases where other treatments have not provided relief.
Physical Therapy for Shoulder Bursitis
Physical therapy plays a pivotal role in treating shoulder bursitis. It involves guided exercises that alleviate pain and improve mobility. One common exercise is the ‘walk-up,’ where you crawl your fingers up a wall to gradually extend your shoulder’s range of motion.
Holding stretches for 15 to 30 seconds can also enhance flexibility in the shoulder region.
Strengthening exercises such as wall pushups and scapular retraction help stabilize the shoulder by engaging the scapular muscles. Using resistance bands for external rotation exercises is crucial for comprehensive rehabilitation. These specific exercises are often included in post-surgery rehabilitation to regain strength and movement.
A physical therapist can create a personalized program to target the specific needs and progress of each patient, ensuring an effective recovery process.
Preventing Shoulder Bursitis
Prevention is always better than cure. Avoiding repetitive overhead movements can significantly reduce the risk of developing shoulder bursitis. Maintaining good posture, whether sitting or standing, helps prevent unnecessary strain on the shoulder joint.
Ergonomic tools and equipment during work-related activities minimize shoulder strain. Simple adjustments like these can go a long way in preventing and maintaining overall shoulder health.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Recognizing when to seek medical attention for shoulder bursitis prevents serious complications. Experiencing symptoms like redness, significant inflammation, fever, or severe pain calls for immediate evaluation. These signs could indicate infected bursitis, which requires prompt medical treatment to prevent the infection from spreading.
Consult a doctor if bursitis symptoms persist for more than a few weeks or if swelling occurs in multiple areas. Early intervention can prevent long-term damage and improve the chances of a full recovery.
Summary
In summary, shoulder bursitis is a common but manageable condition. By understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms early, and following proper treatment and preventive measures, you can significantly reduce its impact on your life. Remember, proactive management and timely medical intervention are key to maintaining shoulder health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is shoulder bursitis?
Shoulder bursitis is an inflammation of the bursa in the shoulder joint, causing pain and limited range of motion. This condition can significantly impact daily activities and should be addressed promptly.
What causes shoulder bursitis?
This condition is often caused by repetitive overhead movements, injuries, and underlying conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis. Addressing these factors can help manage and prevent the condition.
What are common symptoms of shoulder bursitis?
Shoulder bursitis commonly presents with localized pain, swelling, tenderness, and restricted movement, often intensifying at night. It’s important to address these symptoms promptly to prevent further discomfort.
How is shoulder bursitis diagnosed?
Shoulder bursitis is diagnosed through a physical examination, X-rays to identify any calcifications, and MRI scans to visualize the bursa for confirmation.
What treatments are available for shoulder bursitis?
This condition can be effectively treated with a combination of at-home care, such as rest and ice, along with medical interventions like corticosteroid injections and physical therapy. In severe instances, surgical options may be considered.





