Dealing with shoulder pain, but not sure what caused it? In this post, we’ll explore common reasons behind unexplained shoulder discomfort, such as repetitive strain, degenerative changes, and inflammation, and ways to address them.
Key Takeaways
- Shoulder pain can arise from various non-injury-related causes, including repetitive strain, degenerative conditions, and inflammation.
- Common conditions leading to shoulder pain include rotator cuff tendonitis, bursitis, arthritis, frozen shoulder, and calcific tendonitis, each requiring its own treatment approach.
- Initial management of unexplained shoulder pain may involve rest, ice, compression, and elevation (R.I.C.E.), but medical evaluation may be indicated with persistent or worsening symptoms.
Understanding Shoulder Pain
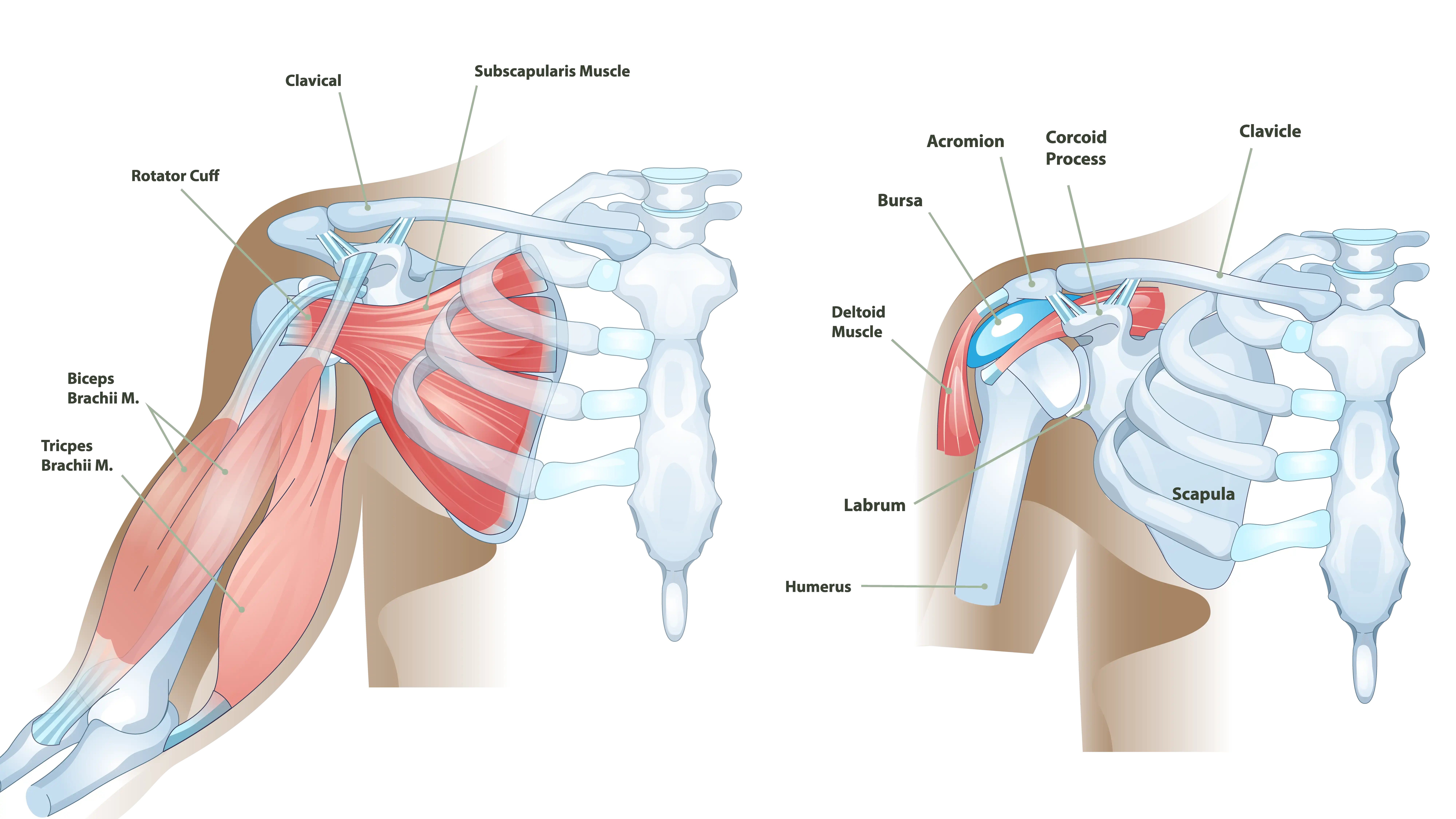
The shoulder is one of the most mobile joints in the body, enabling a wide range of motion for many activities. The shoulder joint is composed of the glenohumeral joint, which includes the upper arm bone (humerus), shoulder blade (scapula), and the socket (glenoid). This ball-and-socket design provides the flexibility to perform everyday tasks but is also susceptible to various issues that can lead to shoulder pain.
Shoulder pain can present in different ways. Individuals may experience a dull ache that makes it hard to sleep on the side, sharp pain when lifting the arm overhead, or even a burning sensation that radiates down the arm.
Many of these symptoms may be linked to repetitive strain, degenerative conditions, or inflammation. Exploring the specific causes of shoulder pain can reveal how different conditions impact the shoulder. In the following sections, we’ll take a closer look at some of the more common shoulder conditions that cause pain.
Rotator Cuff Tendonitis and Bursitis
One of the most frequent causes of non-traumatic shoulder pain is inflammation of the rotator cuff tendons (rotator cuff tendonitis) or the bursa (bursitis).
The rotator cuff is made up of four muscles and their tendons, which stabilize the shoulder and allow for a wide range of movement. Repetitive overhead activities, such as painting or playing tennis, can lead to inflammation of the rotator cuff tendons. This inflammation can cause significant discomfort and restrict the range of motion.
Bursitis occurs when the bursa, a fluid-filled sac that cushions the shoulder joint, becomes inflamed. It often accompanies rotator cuff tendonitis, compounding pain and stiffness.
Treating these conditions typically involves a combination of rest, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications. Physical therapists can guide exercises that strengthen the shoulder muscles and improve flexibility, with the goal of reducing pain and preventing future injuries. In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be recommended for short-term pain relief.
Arthritis in the Shoulder
Arthritis is another possible cause of shoulder pain without a specific injury. This condition involves joint inflammation that can lead to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Arthritis in the shoulder can be particularly debilitating, as it affects the shoulder’s ability to move freely and perform everyday tasks.
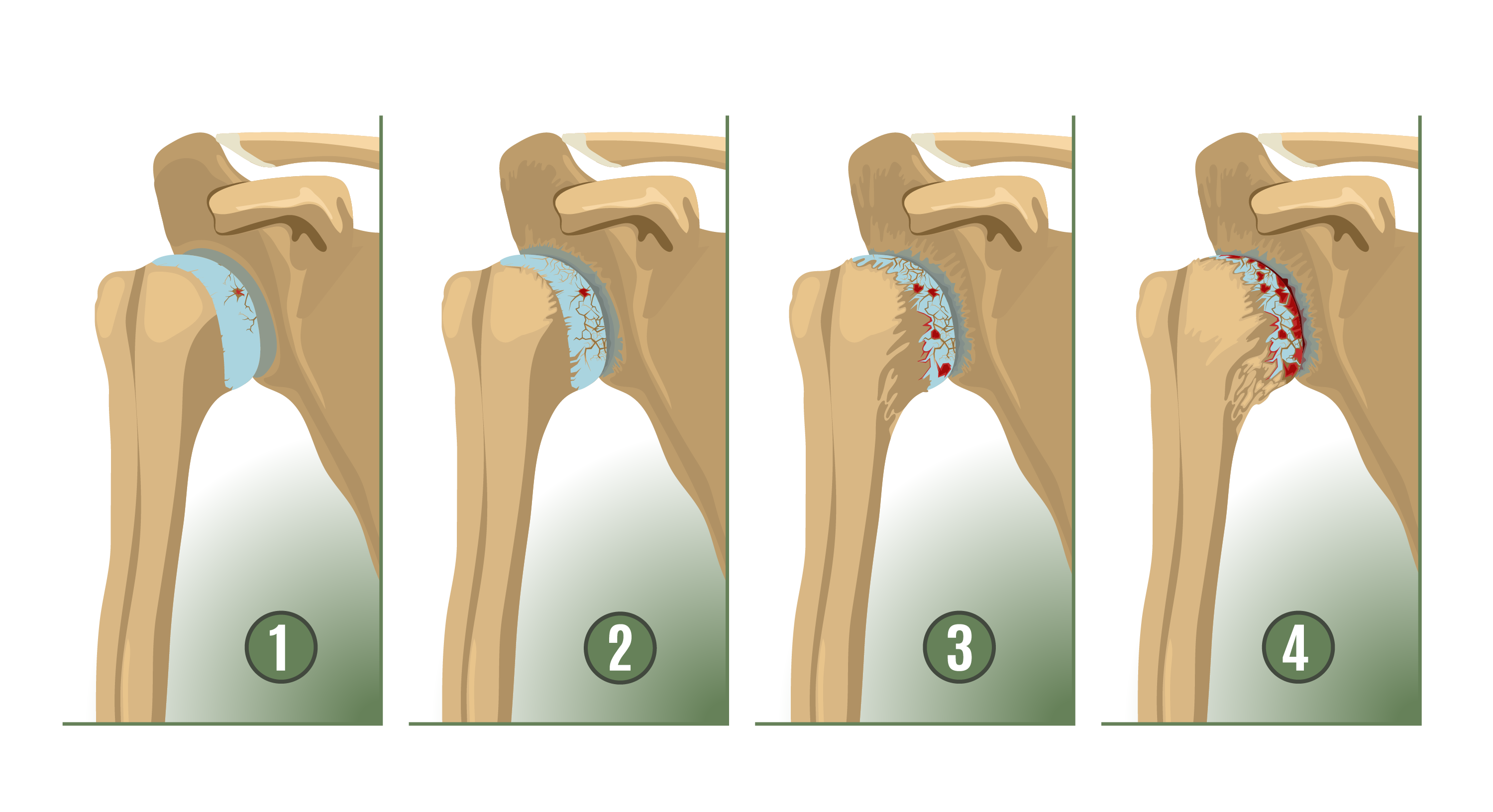
There are different types of arthritis that can affect the shoulder. The two most common types are:
- Osteoarthritis: Typically caused by the gradual wear and tear of the cartilage, leading to bone-on-bone friction and stiffness.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: An autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks the lining of the joints, causing inflammation and pain.
Symptoms of shoulder arthritis may include persistent pain, swelling, and reduced range of motion. Over time, the condition can worsen, making it increasingly difficult to move the shoulder without discomfort.
Treatment options for shoulder arthritis range from lifestyle modifications, physical therapy, and medications to surgical interventions such as total shoulder replacement.
Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis)
Frozen shoulder, also known as adhesive capsulitis, is a condition that may involve thickening and tightening of the shoulder capsule, leading to restricted movement and pain. This condition often develops gradually and can take several months to resolve.
The exact cause of frozen shoulder is not fully understood, but it is believed to result from inflammation in the lining of the shoulder joint. Individuals with frozen shoulder often experience a dull ache that becomes more intense with movement, as well as pain and stiffness.
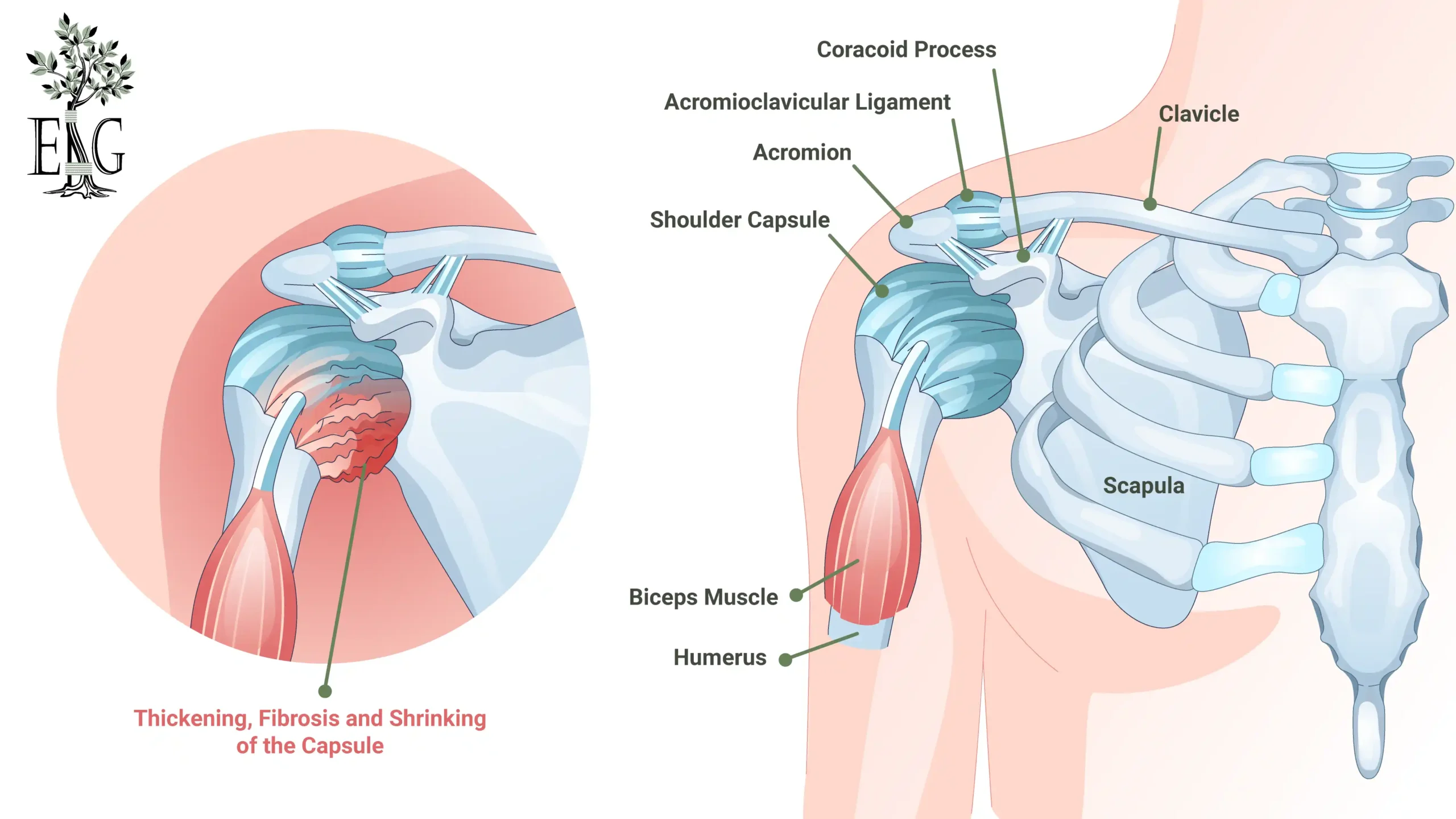
Treating frozen shoulder may involve:
- Physical therapy, focusing on stretching and strengthening the shoulder muscles to improve flexibility and restore movement
- Pain management strategies
- Corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation
- Hydrodilatation, where fluid is injected into the joint
- PRP (platelet-rich plasma) injections with the goal of promoting healing
In some cases where conservative approaches fail to provide relief, surgery such as capsular release may be performed to help relieve pain and stiffness. Manipulation under anesthesia is another procedure that may be recommended for frozen shoulder.
Calcific Tendonitis
Calcific tendonitis is a condition that occurs when calcium deposits form in the shoulder tendons. These calcium deposits can cause intense shoulder pain and limit the shoulder’s range of motion.
The exact cause of calcific tendonitis remains unclear, but it is thought to be related to aging and degenerative changes in the shoulder tendons. Symptoms of calcific tendonitis can include sudden, sharp pain in the shoulder, especially when moving the arm overhead, and a persistent ache that can interfere with sleep.
Diagnosis of calcific tendonitis usually involves imaging tests such as X-rays, which can typically visualize the calcium deposits and confirm the diagnosis. Treatment options may include anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, or procedures to remove the calcium deposits.
Referred Pain
Shoulder pain can sometimes be referred from problems in other parts of the body, a phenomenon known as referred pain. This type of pain occurs when an issue in one area causes discomfort to be felt in another area.
One common source of referred shoulder pain is the cervical spine. Degenerative changes in the spinal discs or nerve compression in the neck can lead to discomfort that radiates to the shoulder area. This type of pain is often described as a dull ache or sharp pain that worsens with certain movements of the neck or shoulder.
Diagnosing referred pain generally involves a thorough physical exam and imaging tests to identify the root cause of the discomfort. Treatment options may include physical therapy, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and, in some cases, surgical intervention. Effective treatment of referred pain typically involves addressing the underlying issue.
Initial Pain Management Strategies
If experiencing shoulder pain without an apparent injury, initial management strategies may help reduce discomfort. The R.I.C.E. method is a commonly recommended approach to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation, consisting of rest, ice, compression, and elevation.
Additionally, over-the-counter pain relief may help with initial pain management. If the pain is severe, persists, or worsens, consider seeking medical evaluation. A physical examination and imaging tests may be indicated for accurate diagnosis, and an experienced shoulder specialist can help guide the most appropriate treatment plan.
Summary
Understanding the various causes of shoulder pain without injury can help you take proactive steps. From rotator cuff tendonitis and bursitis to arthritis and frozen shoulder, each condition requires a unique approach to treatment. By recognizing the symptoms and seeking appropriate medical advice, you can take steps toward effective treatment. Remember, early intervention is key to reducing the risk of long-term issues.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes shoulder pain without injury?
Shoulder pain without injury is often due to conditions like rotator cuff tendonitis, bursitis, arthritis, or frozen shoulder, as well as referred pain from other areas.
How can I treat shoulder pain at home?
R.I.C.E. (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation), over-the-counter pain relief, and gentle stretching are often recommended as initial steps for shoulder pain management. However, if symptoms are severe, persistent, or worsening, it might be time to consider seeking professional medical evaluation.
What are the symptoms of rotator cuff tendonitis?
The symptoms of rotator cuff tendonitis primarily consist of pain when lifting the arm, shoulder weakness, and a restricted range of motion. Clicking or popping sensations during movement may also be experienced.
Could my neck be causing my shoulder pain?
Yes, nerve compression or degenerative changes in the cervical spine can create referred pain that is felt within the shoulder. An accurate diagnosis is important for guiding an appropriate treatment plan.